Researching military personnel
Uncover an individual’s wartime service and experiences with the help of a research guide. Learn how to access and gather information from wartime documentation and modern publications, as well as how to find photographs, works of art, military equipment, and more.
Each guide will walk you through the steps of finding where and when individuals served as well as their unit history, culture, important activities, or battle honours. Learn about training, promotions, medals, injuries and medical treatment, graves and memorials, and the context of their war service.
Prior to the creation of a Canadian navy, Britain’s Royal Navy was responsible for the military defence of Canada’s waters. This changed in 1910 when the federal government passed legislation creating the Naval Service of Canada, which became the Royal Canadian Navy in 1911.
Development and growth was initially slow and so the Royal Canadian Navy had a limited role during the First World War. However, the Second World War created challenges and opportunities that stimulated the Royal Canadian Navy to expand and become the fifth largest navy in the world by 1945, with approximately 1,140 vessels. By the end of the war, over 105,000 men and women had served with the Royal Canadian Navy. Canadian and Allied merchant ships and their crews were also a vital part of the Allied war effort, transporting personnel, munitions, weapons, and food across the world’s oceans.
This guide will illustrate the process of researching an individual’s service, from the essential starting point of service documents to supporting resources for detail and further discovery.
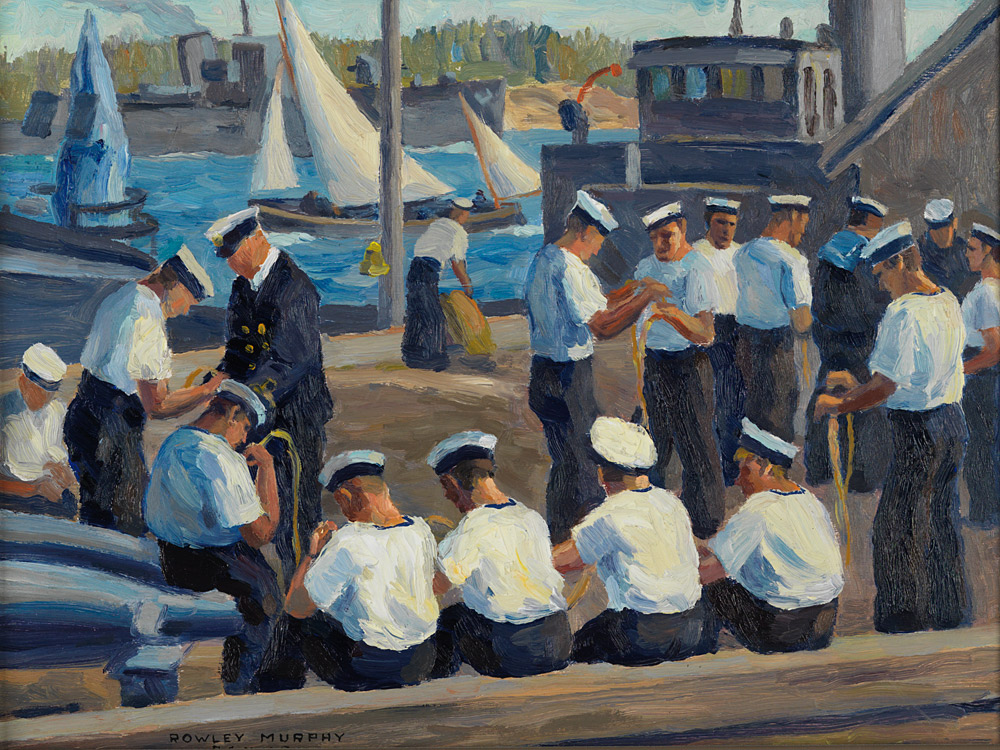
Large-scale military aviation began with the First World War, not long after the 1909 flight of the Silver Dart marked the start of aviation in Canada. As no Canadian Air Force yet existed, thousands of Canadians fought the First World War in British flying units.
Canadians first served with the Royal Flying Corps or with the Royal Naval Air Service. These two services amalgamated on April 1, 1918 into the Royal Air Force. In total, an estimated 13,000 – 22,000 individuals from Canada joined the British flying services.
In 1924, the Royal Canadian Air Force was created. With the outbreak of war in September 1939, the Royal Canadian Air Force was able to draw on an existing cadre of officers and airmen and also attracted experienced personnel from private enterprise. By 1945, close to 250,000 men and women had served in the Royal Canadian Air Force at home and abroad.
This guide will illustrate the process of researching an individual’s service, from the essential starting point of service documents, to supporting resources for detail and further discovery.

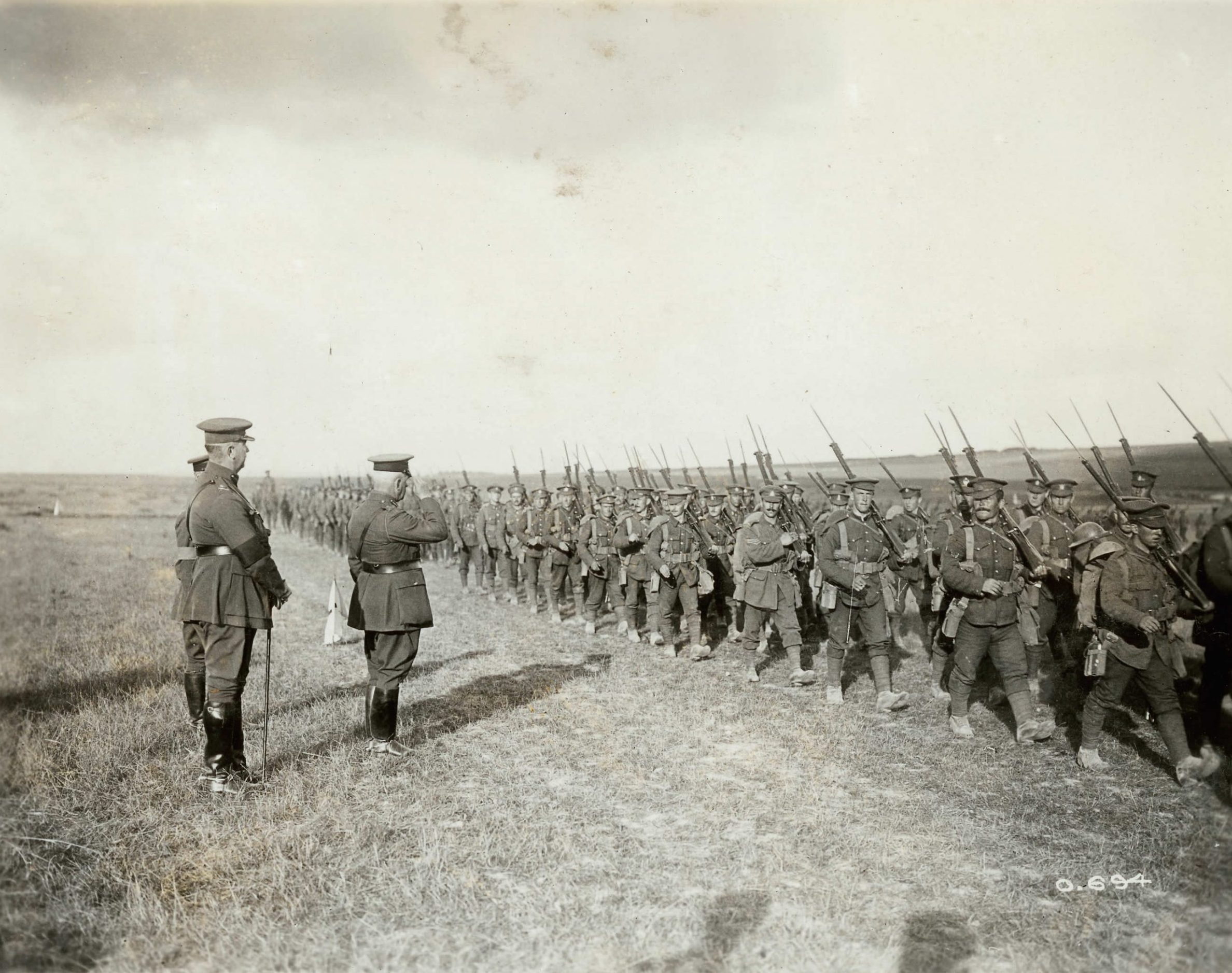
Prior to the First World War, Canada’s defence relied on the British Army and the Canadian militia. A small permanent force was created in the 1870s and by 1914 numbered about 3,000 all ranks. At the declaration of war in 1914, men rushed to join the newly constituted Canadian Expeditionary Force.
In total, over 620,000 men and women served in the CEF, including over 100,000 conscripts. The Canadian Expeditionary Force formed part of the British Expeditionary Force, but most Canadians served within recognizable Canadian units, be it at the battalion, brigade, division, or within the Canadian Corps.
While the Canadian Expeditionary Force was effectively disbanded in 1919, a small core of experienced officers and men remained in the army during the interwar years, and later formed the basis for the Canadian Army in the next war. At the outbreak of war in 1939, Canada’s army was initially known as the Canadian Active Service Force, and from the Fall of 1940, as the Canadian Army. Over the course of the war the Army grew to a force of 730,000 men and women, fought in multiple theatres of war, and made significant contributions to the success of the Allied cause.

Prior to the First World War, few women experienced military service. Twelve women, including trained nurses and Anglican nuns, assisted government forces in nursing capacities during the North-West Resistance in 1885.
During the South African War (1899-1902) 12 trained Canadian nurses were attached to the British medical services. This foreshadowed the significant contributions that Canadian women would make to the war effort in both the First and Second World Wars.
Between 1914 and 1919, more than 3,200 nurses served with the Canadian Army Medical Corps at home and overseas. More than 1,000 also volunteered to serve in British hospitals as nurses and nursing assistants. During the Second World War, while women once again volunteered as nurses, the role of women in the military underwent a significant expansion. The Canadian Army, the Royal Canadian Air Force, and the Royal Canadian Navy created women’s divisions; as a result, about 50,000 women served in a variety of wartime occupations.
This guide will illustrate the process of researching an individual’s service, from the essential starting point of service documents, to supporting resources for detail and further discovery.
